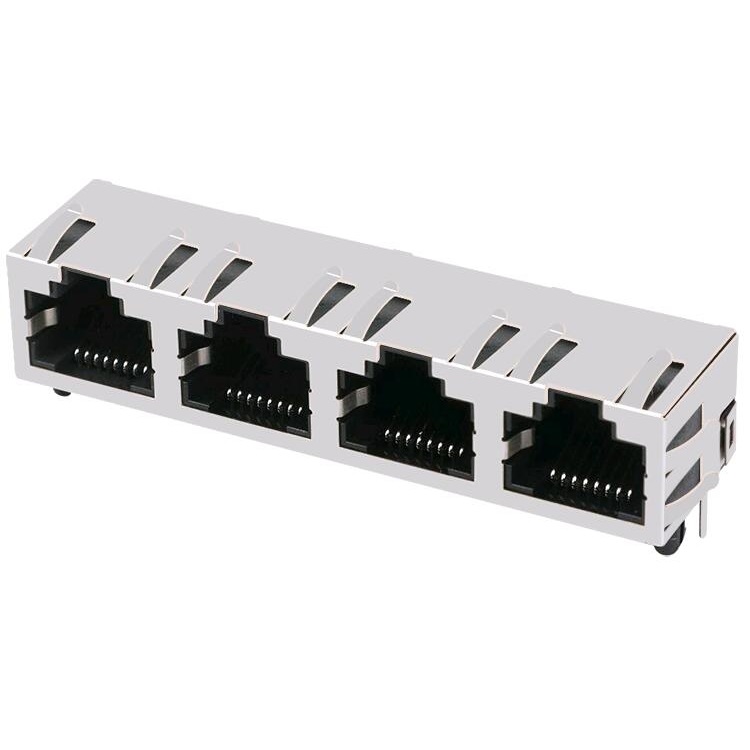
HCJT4-812SK 8P8C Shielded Ganged 1×4 Quad Port Tab-Up RJ45 JACK
HCJT4-812SK 8P8C Shielded Ganged 1×4 Quad Port Tab-Up RJ45 JACK
| Categories | Connectors, Interconnects |
| Modular Connectors - Jacks | |
| Application-LAN | ETHERNET(NoN POE) |
| Connector Type | RJ45 |
| Number of Positions/Contacts | 8p8c |
| Number of Ports | 1×4 |
| Applications Speed | RJ45 Without Magnetics |
| Mounting Type | Through Hole |
| Orientation | 90° Angle (Right) |
| Termination | Solder |
| Height Above Board | 13.40 mm |
| LED Color | Without LED |
| Shielding | Shielded, EMI Finger |
| Features | Board Guide |
| Tab Direction | UP |
| Contact Material | Phosphor Bronze |
| Packaging | Tray |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C ~ 85°C |
| Contact Material Plating Thickness | Gold 6.00µin/15.00µin/30.00µin/50.00µin |
| Shield Material | Brass |
| Housing Material | Thermoplastic |
| RoHS Compliant | YES-RoHS-5 WIth Lead in Solder Exemption |
RJ connector function use: power use
RJ connector is necessary to transmit power. Generally, its voltage is very low. Generally used are the following two power transmission methods: dedicated to high-level current power touch transmission and parallel multilateral signal touch. Each of them has advantages and disadvantages.
There are two differences between power transmission and signal transmission. The first and most notable one is that it is used to deliver higher currents. The current transmitted by the signal generally does not exceed 1 ampere, and does not exceed a few amperes, while the current transmitted by the power can reach tens or even hundreds of amperes. The second is the temperature increase due to Joule heating caused by the current. The Joule heat generated during the signal touch process is similar to the surrounding temperature. Conversely, the ratio of power transmission is based on the addition of temperature, and the increase of temperature generates a corresponding ratio current. The addition of a temperature of 30 degrees is generally used as a current ratio specification.